Japanʼs history for combatting
infectious diseases
In 1930s and 1940s Japan, malaria, TB, schistosomiasis, and
soil-transmitted helminths were endemic.
In order to address these issues, community-based public health programs organized by government leaders,
healthcare professionals, researchers, and individual citizens resulted in the effective elimination
and subsequent eradication of these diseases in Japan in the 1960s and 1970s.
The world recognized Japanʼs recovery and rapid economic growth during the decade following World War II
as nothing short of miraculous.
The countryʼs game-changing post-war public health programs now
form the basis of many WHO disease elimination strategies.
After several decades of increasing scientific and public health successes domestically,
as well as overseas development aid globally, in the 1990s Japan also catalyzed numerous
major global health initiatives, such as the Hashimoto Initiative
to support international parasite control.
Japan also played a major role in creating the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis, and Malaria.
In 2013, GHIT Fund, the world's first public-private global health R&D fund was established.
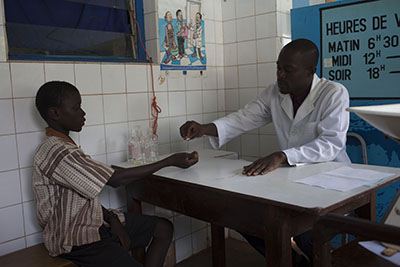
Today, in tireless continuation of its quest to eliminate infectious diseases,
the GHIT Fund serves as a catalyst to the development of new
and much needed pharmaceuticals
for global health by leveraging Japanʼs
technology and innovation.
1930
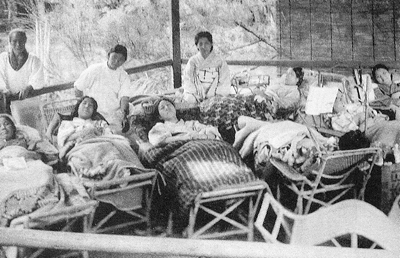
- 1930
- Tuberculosis: The #1 killer Tuberculosis: Over 250,000 die annually, over 1.5 million infected
1945

- 1945
- Over 70% of Japan's population, infected with Soil Transmitted Helminths Over 400,000 soldiers return, infected with Malaria
1948
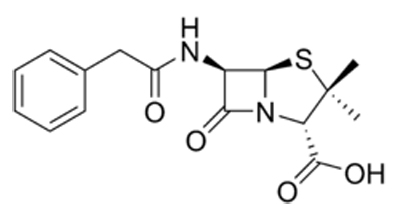
- 1948
- Self-sufficient in penicillin production Fewer deaths by infectious disease
1949
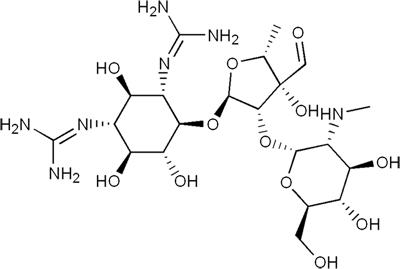
- 1949
- ‘No Flies, No Mosquitoes’ campaign of DDT spraying starts Streptomycin introduced clinically in Japan Drastic reduction of deaths by Tuberculosis
1950

- 1950
- Japan synthesizes Supatonin [Diethylcarbamazine (DEC) citrate] for ascariasis and lymphatic filariasis
1951

- 1951
- Japan Antituberculosis Association formed, Tuberculosis Prevention Act enacted
1955

- 1955
- Founding of Japan Association of Parasite Control (JAPC)

- 1955
- Water Supply Law enacted
1958

- 1958
- Universal Healthcare insurance achieved

- 1958
- School Health Law enacted
1961
- 1961
- Japan eradicates Malaria
1965

- 1965
- Start of ‘Zero parasite’ campaign in Okinawa
1973
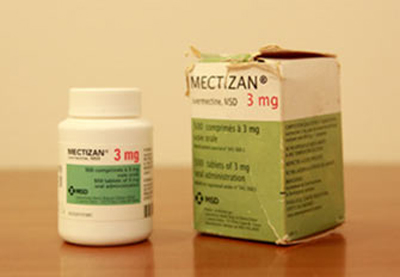
- 1973
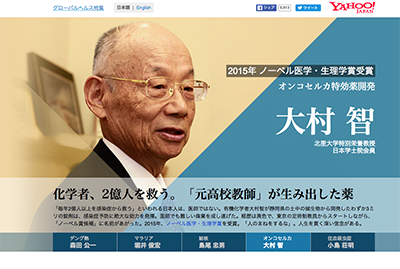
- Professor Omura of Kitasato University discovers Streptomyces avermectinius, the active ingredient of avermectin
1974

- 1974
- Asian Parasitology Control Organization (APCO) launched
1977

- 1977
- Japan eradicates Schistosomiasis
1978

- 1978
- Japan eradicates Lymphatic Filariasis
1980

- 1980
- Global elimination of smallpox
1989
- 1989
- To eradicate Guinea worm in West Adrica, Japan committed 100 million Yen/ 8 years for grant aid
1996
- 1996
- Prevalence of soil-transmitted helminth decreased by 0.01% in Japan
2000
- 2000
- Asian Centre of International Parasite Control established in Thailand
2001
- 2001
- Eastern and Southern Africa Centre of International Parasite Control (ESACIPAC) established at the Kenya Medical Research Institute (KEMRI), Nairobi
2004
- 2004
- West African Centre for International Parasite Control (WACIPAC) established at the Noguchi Memorial Institute for Medical Research, Accra, Ghana
2012
2012.7
- July, 2012
- GHIT Fund Launch Committee established
2013
2013.2
- February, 2013
- Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) reported throughout Saudi Arabia
2013.4

- April, 2013
- GHIT Fund, the world's first public-private global health R&D fund launches. Government of Japan (Ministry of Foreign Affiars and Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, UNDP, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Astellas, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Shionogi and Takeda are GHIT's founding partners
- April, 2013
- Screening Platform Launches

- April, 2013
- Product Development Platform Launches
2013.5

- May, 2013
- Financial Times
Japan in pioneering partnerships to fund global health research
- May, 2013
- Japan developed the Strategy for Global Health Diplomacy
2013.6
- June, 2013
- Japan developed the Revitalization Strategy
2013.11
2013.12
2014
2014.1
- January, 2014
- Dr. Piot receives 2013 Prince Mahidol Award in the field of public health
2014.3
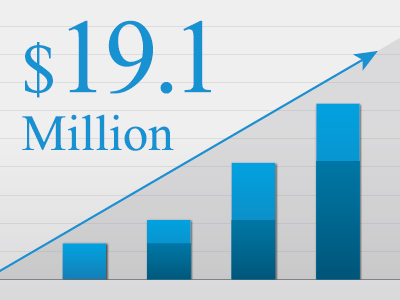
- March, 2014
- Cumulative Investment USD 19.1 Million

- March, 2014
- Cumulative Number of Invested Partnerships
- March, 2014
- Hit-to-Lead Platform Launches
2014.4

- April, 2014
- GHIT and other global health organizations in Tokyo convene charity dinner for 2014 World Malaria Day in Tokyo
2014.6

- June, 2014
- GHIT Hosts GHIT's first anniversary event “Global Health R&D Showcase” in Tokyo
2014.7
- July, 2014
- Japan developed the Healthcare and Medical Strategy
2014.8

- August, 2014
- GHIT convenes 1st proposal writing seminar at the University of Tokyo

- August, 2014
- Dengue fever reported in Japan for the first time in 70 years
2014.11

- November, 2014
- GHIT convenes 2nd proposal writing seminar at the Joint conference of the 55th Annual Meeting of Japanese Society of Tropical Medicine and the 29th Annual Meeting of the Japan Association for International Health
2015
2015.2

- February, 2015
- Target Research Platform Launches
2015.3
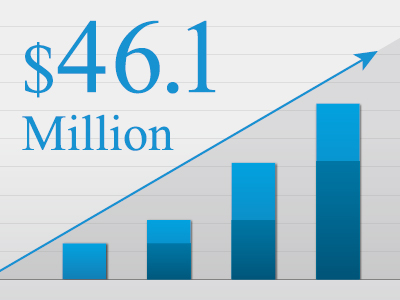
- March, 2015
- Cumulative Investment USD 46.1 Million

- March, 2015
- Cumulative Number of Invested Partnerships
2015.4

- April, 2015
- GHIT convenes 3rd proposal writing seminar in Osaka

- April, 2015
- GHIT leaders discuss Japan's private sector's contribution to global health R&D at World Health Summit Regional Meeting in Kyoto
2015.6

- June, 2015
- GHIT hosts Annual Partners Meeting 2015: Japan's R&D Innovation for Global Health

- June, 2015
- 41st G7 summit takes place in Schloss Elmau, Germany
2015.9

- September, 2015
- United Nations General Assembly adopts Sustainable Development Goals
2015.10
2016
2016.2

- February, 2016
- Zika outbreaks occur in Latin America. WHO declares Public Health Emergency of International Concern in February 2015.

- February, 2016
- GHIT convenes 4th proposal writing seminar at the University of Tokyo
2016.3
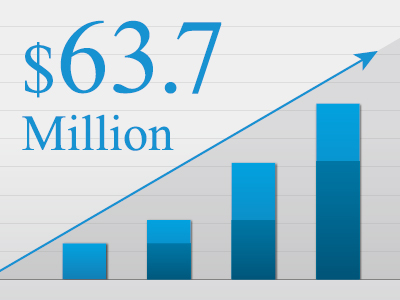
- March, 2016
- Cumulative Investment USD 63.7 Million

- March, 2016
- Cumulative Number of Invested Partnerships
2016.6

- June, 2016
- GHIT convenes 5th proposal writing seminar at the University of Tokyo
2016.8
2017
2017.2

- February, 2017
- GHIT convenes 6th proposal writing seminar at Osaka University
2017.3

- March, 2017
- Cumulative Number of Invested Partnerships